Remote Procedure Calls
AutoSuggest, for its SuggestOracle, fetches a list of symbol names
from a mock datastore SymbolDatabase. In this section, we move
SymbolDatabase to server and fetch list from the server via Remote
Procedure Call (RPC).
GWT RPC Tutorial
GWT StockWatcher tutorial has a gentle introduction to client-server communication. . If you are new to GWT, then it is a prerequisite to cover the RPC section - Making Remote Procedure Calls of the StockWatcher tutorial.
Refactor shared classes
SymbolDatabase, utility class SymbolHelper and domain classes like
Symbol, DataGroup, etc. are in in.fins.client package, but server
also require access these classes. Server uses domain classes, Symbol,
DataGroup, Data and Fact, as Data Access Object (DAO) to hold and send
the data to clients, and clients access these objects to display the
data. Both server and client use SymbolHelper, a utility class, to
access Symbol and its members. For the time being, both sides require
SymbolDatabase as we move only one call to the server in this section.
Server can access these classes even if they are in client package as
all classes lands in the server, but as a good practice, place them in a
shared package. Create a package
in.fins.shared and move the following classes to shared package using
Eclipse’s Refactor-Move feature.
in.fins.client.Symbol
in.fins.client.DataGroup
in.fins.client.Data
in.fins.client.Fact
in.fins.client.SymbolDatabase
in.fins.client.SymbolHelper
To move, select these classes and right click to invoke context menu and choose Refactor → Move. In Move dialog select in.fins.shared package as destination and click OK button.
GWT allow the clients to access these classes only if they are
translatable to javascript. Modify GWT module file - fins.gwt.xml and
add the following to make in.fins.shared package as translatable.
in.fins/fins.gwt.xml
....
<source path="shared" />
....
RPC
GWT Remote Procedure call (RPC) involves four steps.
define client side interfaces.
implement server side service.
configure service.
invoke service from client through async interface.
Client side interfaces
On the client side, we require an interface to interact with the service available on the server which provides a list of symbol names and let’s name the interface as ISymbolService as the task is loosely relates to symbol.
As a good practice, place client side RPC interfaces in a separate
package. For this, create a new package
in.fins.client.rpc. To create interfaces, right click on
in.fins.client.rpc package and choose New → Interface. In
Interface dialog enter name ISymbolService and also, extend interface
com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.RemoteService. Modify the interface and
add a annotation @RemoteServiceRelativePath(“symbolService”).
Annotation associates the service with a default path relative to the
module base URL which we are going to use to configure the service
later. Next, add a service method, getSymbolNames() to the interface,
which clients invoke to get the list of symbol.
in.fins.client.rpc/ISymbolService.java
package in.fins.client.rpc;
import java.util.List;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.RemoteService;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.RemoteServiceRelativePath;
@RemoteServiceRelativePath("symbolService")
public interface ISymbolService extends RemoteService {
public List<String> getSymbolNames() throws Exception;
}
Server side service implements ISymbolService and client use the
interface to create a proxy service, and we require one more async
interface to make RPC calls.
Eclipse Quick Fix feature comes handy to define the async interface. ISymbolService shows an error, Missing asynchronous interface ISymbolServiceAsync, go ahead, and click on error icon to get drop down with four fixes.
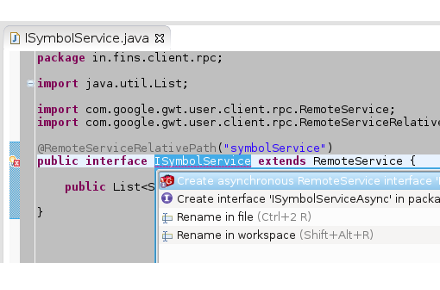
Figure 7.1. Quick Fix
Choose - Create asynchronous RemoteService interface to create
ISymbolServiceAsync. Async interface is a plain interface which
slightly redefines ISymbolService methods.
in.fins.client.rpc/ISymbolServiceAsync.java
package in.fins.client.rpc;
import java.util.List;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.AsyncCallback;
public interface ISymbolServiceAsync {
void getSymbolNames(AsyncCallback<List<String>> callback);
}
While the name and parameters are identical, the async methods have no
return type and last parameter is an AsyncCallback object. We will soon
explain the significance of AsyncCallback, and for the moment it is
suffice to know the differences in method definitions.
To summarize, we defined two interfaces; ISymbolService with required
service methods and its companion an async interface
ISymbolServiceAsync. While service implements ISymbolService, clients
use it to create a proxy service and use ISymbolServiceAsync to invoke
the service method.
Server side service
Create a new package
in.fins.server.service
to place services. Please note that, there is no source entry in
fins.gwt.xml for this package. Hence this package is not translatable to
javascript and only, server has access to it.
Create service class SymbolService and let it implement the interface
ISymbolService.
in.fins.server.service/SymbolService.java
package in.fins.server.service;
import in.fins.client.rpc.ISymbolService;
import in.fins.shared.SymbolDatabase;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import com.google.gwt.user.server.rpc.RemoteServiceServlet;
public class SymbolService extends RemoteServiceServlet implements
ISymbolService {
private static final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(SymbolService.class
.getName());
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public SymbolService() {
super();
}
@Override
public List<String> getSymbolNames() throws Exception {
try {
List<String> list = SymbolDatabase.getSymbolNames();
log.info("Symbol Names : " + list.size());
return list;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warning(e.getMessage());
throw e;
}
}
}
GWT RPC service has to extend RemoteServiceServlet which takes care of
deserialize incoming requests from the client and serialize outgoing
responses. Service method getSymbolNames() obtains list of symbol
names from SymbolDatabase and RemoteServiceServlet serializes the list
before sending it to the client.
SerializableException
GWT RPC requires that all service method parameters and return types be
Serializable so as to serialize all objects that it transfers between
client and server, and throws SerializableException when it finds that
certain type is not Serializable. For this reason, domain classes
Symbol, Data, DataGroup and Fact implements Serializable interface.
Refer Serializing Java objects to know more.
Configure service
SymbolService is a servlet as it extends RemoteServiceServlet and we
have to configure the servlet in web.xml like any other servlet.
Modify web.xml as follows.
war/WEB-INF/web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" standalone="no"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" version="2.5"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>Fins.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>symbolService</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>in.fins.server.service.SymbolService</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>symbolService</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/fins/symbolService</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
ISymbolService contains @RemoteServiceRelativePath(“symbolService”) annotation, and we use the path i.e. symbolService in url-pattern which assists GWT to link the service to a specific servlet.
Invoke service
With all that RPC scaffolding in place, we are finally ready to invoke
the service. Modification to AutoSuggest.setSymbolNames() method
involves three parts.
create an instance of service proxy class.
setup the callback object.
call the service method.
in.fins.client.widget/AutoSuggest.java
private void setSymbolNames() {
// create service Proxy ISymbolServiceAsync symbolService = GWT.create(ISymbolService.class);
// call service method symbolService.getSymbolNames(new AsyncCallback<List<String>>() {
// setup callback object @Override
public void onSuccess(List<String> list) {
((MultiWordSuggestOracle) suggestBox.getSuggestOracle())
.addAll(list);
log.fine("Received symbol names via RPC");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable caught) {
log.warning(caught.getMessage());
}
});
}
| GWT.create() method creates the service proxy. Note that we use ISymbolService in create() method but returned proxy object is assigned to ISymbolServiceAsync. GWT.create() does this trick via a concept known as deferred binding. |
| Remote call is async in nature as clients doesn't know when server returns the service request. To accomodate this, you have to specify a callback method which executes when remote call completes. Callback object is anonymous inner type AsyncCallBack with two overloaded methods onSuccess() and onFailure(). Success method receives the object returned by the service and failure method receives any exception encountered by the server or RPC call. |
| Service method getSymbolNames() is called. Method onSuccess() receives the List<String> that is set to SuggestionOracle. |
On app access, a log message in Eclipse console displays the size of the list and another message in the log tab confirms that client has indeed received the list via RPC. Server side logs are sent to console while client logs are sent to three locations; console, Development Mode view and log tab. Console distinguishes logs by showing server logs in red font and client logs in black font.


